Active components
Active components rely on a source of energy (usually from the DC circuit, which we have chosen to ignore) and usually can inject power into a circuit, though this is not part of the definition. Active components include amplifying components such as transistors, triode vacuum tubes (valves), and tunnel diodes
Active components we were using in previous topic and will use in the following topics:
- Light-emitting diode (LED);
- LED display;
Light-emitting diode (LED)
Is a semiconductor light source that emits light when
current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with
electron holes, releasing energy in the form of photons. The color of the light
(corresponding to the energy of the photons) is determined by the energy
required for electrons to cross the band gap of the semiconductor. White
light is obtained by using multiple semiconductors or a layer of light-emitting
phosphor on the semiconductor device.
LEDs are used in applications as diverse as aviation
lighting, fairy lights, automotive headlamps, advertising, general lighting,
traffic signals, camera flashes, lighted wallpaper, horticultural grow lights,
and medical devices.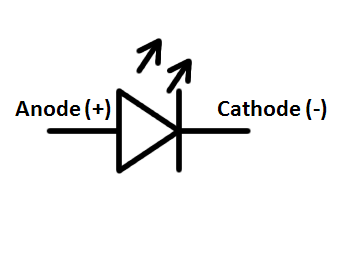
Parts of a conventional LED. The flat bottom surfaces of the anvil and post embedded inside the epoxy act as anchors, to prevent the conductors from being forcefully pulled out via mechanical strain or vibration.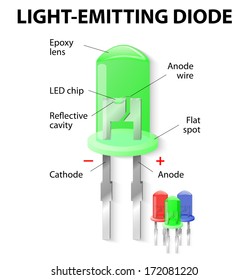
LED display
A LED display is a flat panel
display that uses an array of light-emitting diodes as pixels for a video
display. Their brightness allows them to be used outdoors where they are
visible in the sun for store signs and billboards. In recent years, they have
also become commonly used in destination signs on public transport vehicles, as
well as variable-message signs on highways. LED displays are capable of
providing general illumination in addition to visual display, as when used for
stage lighting or other decorative (as opposed to informational) purposes. LED
displays can offer higher contrast ratios than a projector and are thus an
alternative to traditional projection screens, and they can be used for large,
uninterrupted (without a visible grid arising from the bezels of individual
displays) video walls. microLED displays are LED displays with smaller LEDs,
which poses significant development challenges.
Detail view of a LED display with a matrix of red, green and blue diodes.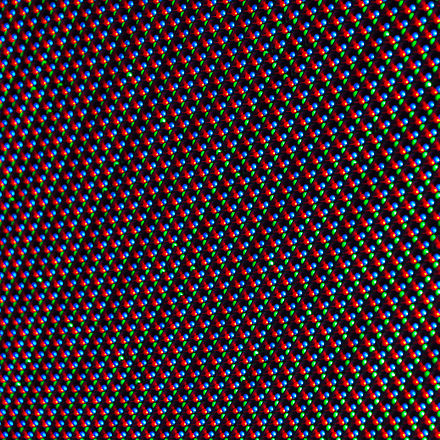
A seven-segment display
Is a form of electronic display device for displaying decimal numerals that is an alternative to the more complex dot matrix displays.
Seven-segment displays are widely used in digital clocks, electronic meters, basic calculators, and other electronic devices that display numerical information.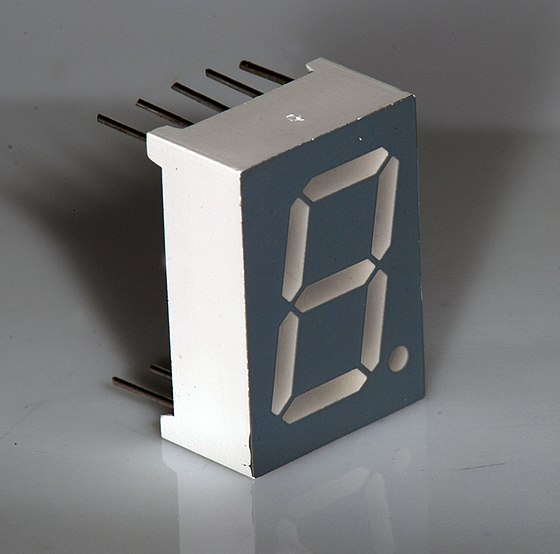
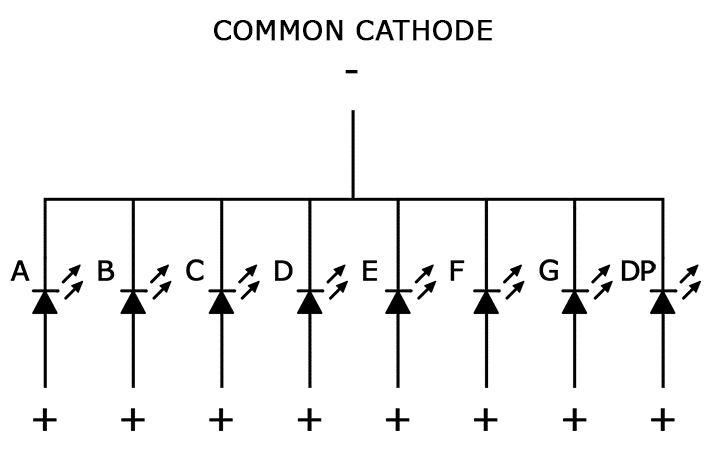
Common cathode displays
In common cathode displays, all of the cathodes are connected to ground and individual segments are turned on and off by switching power to the anodes:
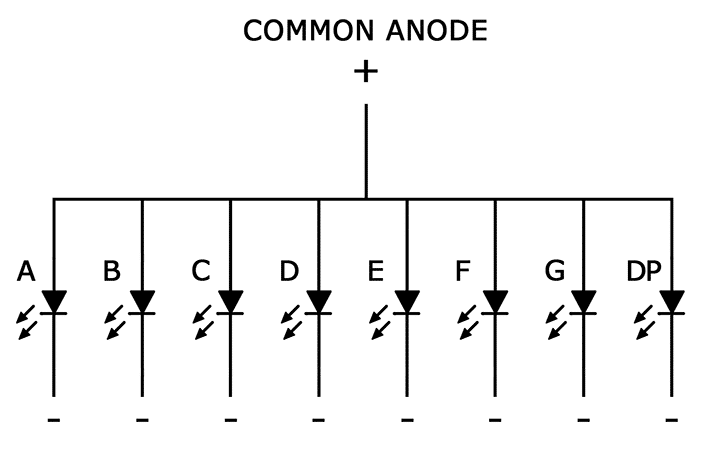
Common anode displays
In common anode displays, all of the anodes are connected to Vcc, and individual segments are turned on and off by switching power to the cathodes:
Before use seven-segment display, you need to determine if a display is common anode or common cathode, we will do it in seven-segment display circuit.
