Sensors
In the broadest definition, a sensor is a device,
module, machine, or subsystem whose purpose is to detect events or changes in
its environment and send the information to other electronics, frequently a
computer processor. A sensor is always used with other electronics.
Sensors we were using in previous topic and will use in the following topics:
- Ultrasonic distance sensor;
- TCS3200 Color Sensor.
Ultrasonic distance sensor
An ultrasonic sensor is an instrument that measures the distance to an object using ultrasonic sound waves.
An ultrasonic sensor uses a transducer to send and receive ultrasonic pulses that relay back information about an object’s proximity.
High-frequency sound waves reflect from boundaries to produce distinct echo patterns.

Ultrasonic sensors work by sending out a sound wave at a frequency above the range of human hearing. The transducer of the sensor acts as a microphone to receive and send the ultrasonic sound.
TCS3200 Color Sensor
TCS3200 chip is designed to detect the color of light incident on it. It has an array of photodiode (a matrix of 8x8, so a total 64 sensors). These photodiodes are covered with four type of filters. Sixteen sensor have RED filter over them thus can measure only the component of red in the incident light. Like wise other sixteen have GREEN filter and sixteen have BLUE filter. As you should know that any visible colour can be broken into three primary colours. So these three type of filtered sensors helps measure the weightage of each of primary colours in incident light. The rest 16 sensors have clear filter.
TCS3200 converts the intensity of incident radiation into frequency. The output waveform is a 50% duty cycle square wave. You can use the timer of a MCU to measure period of pulse and thus get the frequency. The output of TCS3200 is available in single line. So you would ask how we get the intensity of RED,GREEN, BLUE and CLEAR channels Well it has two inputs S2 and S3 that is used to select the sensor whose output need to be made available on the out line.
PinOut
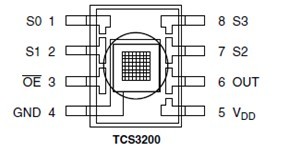
| Pin Name | I/O | DESCRIPTION |
| GND(4) | Power supply ground. All voltages are referenced to GND | |
| OE(3) | I | Enable for fo (active low). |
| OUT | O | Output frequency (fo). |
| S0,S1(1,2) | I | Output frequency scaling selection inputs. |
| S2,S3(7,8) | I | Photodiode type selection inputs |
| VDD(5) | Supply voltage |
