2D figures
Types of 2D Shapes
2D shapes are flat and can be drawn on a sheet of paper. There are different types of regular and irregular 2D shapes like a circle, triangle, square, rectangle, pentagon, quadrilateral, and hexagon. Let us study each of them in detail.
2D Shapes
A 2D (two-dimensional) shape is a flat shape that has only two dimensions – length and width, with no thickness or depth. For example, a sheet of paper is two dimensional in shape. It consists of a length and a width but does not have any depth or height. Some common 2D shapes are square, rectangle, triangle, circle, and hexagon. In comparison to these, a 3D (three-dimensional) shape has three dimensions – length, width, and height. For example, a dice is three-dimensional because it consists of a length, a width, and a height. Some common 3D shapes are cuboid, cone, pyramid, and cylinder.
2D Shapes Definition
In geometry, 2D shapes can be defined as plane figures that are completely flat and have only two dimensions – length and width. They do not have any thickness and can be measured only by the two dimensions. A polygon is a 2D shape made up of straight-line segments which are connected with each other, thus giving it a closed shape. A circle, square, rectangle, and triangle are some examples of two-dimensional objects and these shapes can be drawn on paper. All the 2D shapes have sides, vertices (corners), and internal angles, except for the circle, which is a curved figure. 2D Shapes with at least three straight sides are called polygons and that includes triangles, squares, and quadrilaterals.
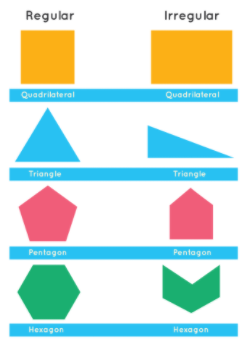
Regular and Irregular 2D Shapes
A 2D shape can be classified as regular or irregular based on the length and the interior angles:
- A 2D shape is said to be regular if all its sides are equal in length and all its interior angles measure the same.
- A 2D shape is irregular if all the sides are of unequal length and all its angles are of unequal measures.
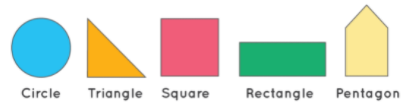
Types of 2D Shapes
2D shapes are flat and can be drawn on a sheet of paper. There are different types of regular and irregular 2D shapes like a circle, triangle, square, rectangle, pentagon, quadrilateral, and hexagon.
Circle:
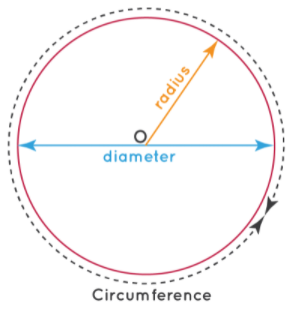
A circle is a closed 2D shape made up of a curved line with no corners or edges. Some real-life examples of the circle are coins, wheels, and pizzas. A circle consists of various parts like the radius, diameter, circumference, and so on:
- The circumference is the length of the boundary of the circle.
- The radius is the distance from the center of the circle to the boundary of the circle.
- The diameter is a line segment that goes straight across the circle, through the center. It is the longest possible line that can be drawn inside a circle and is twice the length of the radius.
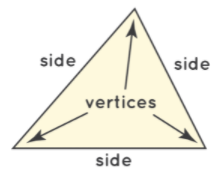
A triangle is a 2D shape with three sides and three vertices (corners). It is a polygon whose interior angles add up to 180°.
Square:
A square is a 2D shape with four equal sides and each angle is equal to 90˚. Some of the real-life examples of a square are: a loaf of bread and a chessboard.
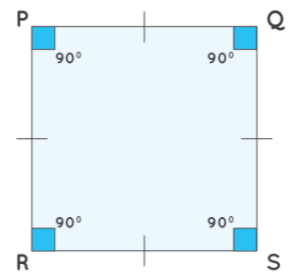
Observe the given square PQRS and note the following properties:
- All four sides are equal, i.e., side PQ = QS = RS = PR
- Side PQ is parallel to RS.
- Side PR is parallel to QS.
- All four internal angles measure 90 ̊.
Rectangle:
A rectangle is a 2D shape with four sides in which the opposite sides are equal and parallel, and all the four angles measure 90 ̊. Some of the real-life examples of a rectangle are table tops, blackboard, cardboard, etc.
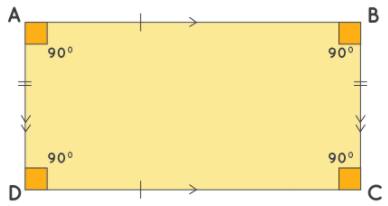
Observe the given rectangle ABCD and note the following properties:
- Side AB = DC
- Side AD = BC
- Side AB is parallel to DC.
- Side AD is parallel to BC.
- All four angles measure 90 ̊.
Pentagon:
Pentagon is a 2D closed polygon with five sides and five interior angles. Some of the real-life examples of a pentagon are the black sections on soccer balls, school crossing signs, the Pentagon building in the US, etc.
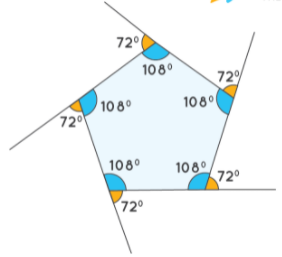
Observe the given regular pentagon and note the following properties:
- All five sides are equal in length.
- Each interior angle measures 108°.
- Each exterior angle measures 72°.
Hexagon:
A hexagon can be defined as a 2D polygon with six sides, six vertices and six angles. Some of the real-life examples of a hexagon are the honeycomb cells and metal nuts.
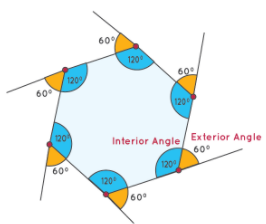
Observe the given regular hexagon and note the following properties:
- All six sides are equal in length.
- Each interior angle measures 120°.
- Each exterior angle measures 60°.
Link
